Harlequin-type Ichthyosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Harlequin-type ichthyosis is a
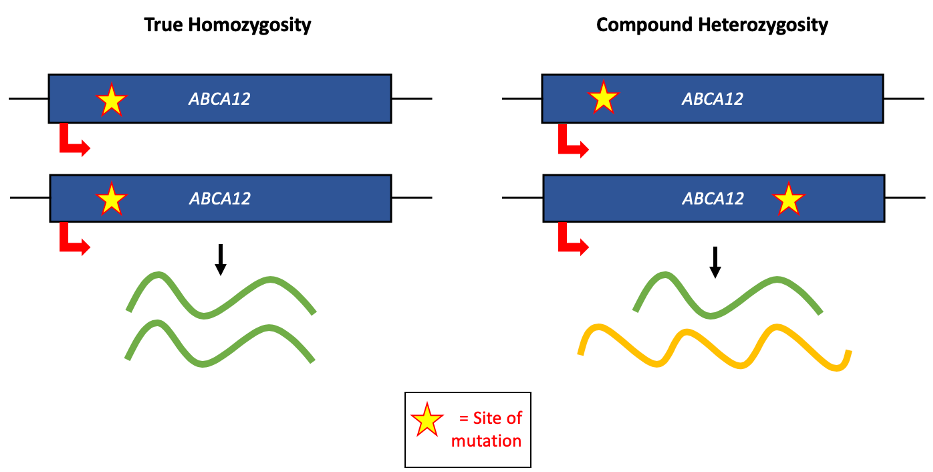 Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ''
Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ''
File:Illustrated Medicine and Surgery (1888) (14784247353).jpg, Female case, 1888
File:Manual of antenatal pathology and hygiene - the foetus (1902) (14784556735).jpg, Male case, 1902
File:Kyber's case of foetal ichthyosis.jpg, Kyber's case, 1902
File:TJOD-14-138-g4.jpg, An infant with Harlequin ichthyosis.
File:Harlequin ichtyosis.jpg, An infant with Harlequin ichthyosis.
File:Harlequin ichthyosis.png, Harlequin ichthyosis in a female infant
File:TJOD-14-138-g1.jpg, Harlequin ichthyosis in a male infant
File:TJOD-14-138-g3.jpg, An infant with Harlequin ichthyosis covered in sterile gauze.
File:Harlequin ichthyosis (2).png, Harlequin ichthyosis in a 3-year-old girl, the keratin scales having almost completely fallen off
Information
from the U.S.
genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
that results in thickened skin over nearly the entire body at birth. The skin forms large, diamond/trapezoid/rectangle-shaped plates that are separated by deep cracks. These affect the shape of the eyelids, nose, mouth, and ears and limit movement of the arms and legs. Restricted movement of the chest can lead to breathing difficulties. These plates fall off over several weeks. Other complications can include premature birth
Preterm birth, also known as premature birth, is the birth of a baby at fewer than 37 weeks gestational age, as opposed to full-term delivery at approximately 40 weeks. Extreme preterm is less than 28 weeks, very early preterm birth is between ...
, infection, problems with body temperature, and dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
. The condition is the most severe form of ichthyosis
Ichthyosis is a family of genetic skin disorders characterized by dry, thickened, scaly skin. The more than 20 types of ichthyosis range in severity of symptoms, outward appearance, underlying genetic cause and mode of inheritance (e.g., dominant ...
, a group of genetic disorders characterised by scaly skin.
Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by mutations in the ''ABCA12
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCA12'' gene.
ABCA12 belongs to a group of genes called the ATP-binding cassette family, which makes ...
'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
. This gene codes for a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
necessary for transporting
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, a ...
lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
out of cells in the outermost layer of skin. The disorder is autosomal recessive
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant ( allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant an ...
and inherited from parents who are carriers. Diagnosis is often based on appearance at birth and confirmed by genetic testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or ...
. Before birth, amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is n ...
or ultrasound
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies ...
may support the diagnosis.
There is no cure for the condition. Early in life, constant supportive care
Symptomatic treatment, supportive care, supportive therapy, or palliative treatment is any medical therapy of a disease that only affects its symptoms, not the underlying cause. It is usually aimed at reducing the signs and symptoms for the comf ...
is typically required. Treatments may include moisturizing cream, antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s, etretinate
Etretinate (trade name Tegison) is a medication developed by Hoffmann–La Roche that was approved by the FDA in 1986 to treat severe psoriasis. It is a second-generation retinoid. It was subsequently removed from the Canadian market in 1996 and ...
or retinoids
The retinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are vitamers of vitamin A or are chemically related to it. Retinoids have found use in medicine where they regulate epithelial cell growth.
Retinoids have many important functions throughou ...
. Around half of those affected die within the first few months; however, retinoid treatment can increase chances of survival. Children who survive the first year of life often have long-term problems such as red skin, joint contractures
In pathology, a contracture is a permanent shortening of a muscle or joint. It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions like sp ...
and delayed growth. The condition affects around 1 in 300,000 births. It was first documented in a diary entry by Reverend Oliver Hart in America in 1750.
Signs and symptoms
Newborns with harlequin-type ichthyosis present with thick, fissured armor-platehyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
. Sufferers feature severe cranial and facial deformities. The ears may be very poorly developed or absent entirely, as may the nose. The eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eye ...
s may be everted (ectropion
Ectropion is a medical condition in which the lower eyelid turns outwards. It is one of the notable aspects of newborns exhibiting congenital Harlequin-type ichthyosis, but ectropion can occur due to any weakening of tissue of the lower eyelid ...
), which leaves the eyes and the area around them very susceptible to infection. Babies with this condition often bleed during birth. The lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ...
s are pulled back by the dry skin (eclabium
Eclabium means the turning outwards of the lip. Eclabium comes from the Greek word "ek" meaning "out," and the Latin word "labium" meaning "lip." This deformation occurs in most babies born with Harlequin type ichthyosis, caused by genetic defec ...
).
Joints are sometimes lacking in movement, and may be below the normal size. Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (from Ancient Greek ὑπo- ''hypo-'' 'under' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ.Polydactyly
Polydactyly or polydactylism (), also known as hyperdactyly, is an anomaly in humans and animals resulting in supernumerary fingers and/or toes. Polydactyly is the opposite of oligodactyly (fewer fingers or toes).
Signs and symptoms
In hum ...
has also been found on occasion. In addition, the fish mouth appearance, mouth breathing, and xerostomia
Xerostomia, also known as dry mouth, is dryness in the mouth, which may be associated with a change in the composition of saliva, or reduced salivary flow, or have no identifiable cause.
This symptom is very common and is often seen as a side eff ...
place affected individuals at extremely high risk for developing rampant dental decay.
Patients with this condition are extremely sensitive to changes in temperature due to their hard, cracked skin, which prevents normal heat loss. The skin also restricts respiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
, which impedes the chest wall
The thoracic wall or chest wall is the boundary of the thoracic cavity.
Structure
The bony skeletal part of the thoracic wall is the rib cage, and the rest is made up of muscle, skin, and fasciae.
The chest wall has 10 layers, namely (from s ...
from expanding and drawing in enough air. This can lead to hypoventilation
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
and respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
. Patients are often dehydrated
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
, as their plated skin is not well suited to retaining water.
Cause
 Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ''
Harlequin-type ichthyosis is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the ''ABCA12
ATP-binding cassette sub-family A member 12 also known as ATP-binding cassette transporter 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ABCA12'' gene.
ABCA12 belongs to a group of genes called the ATP-binding cassette family, which makes ...
'' gene. This gene is important in the regulation of protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical ...
for the development of the skin layer. Mutations in the gene cause impaired transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land ( rail and road), water, cable, pipelin ...
of lipids
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids in ...
in the skin layer and may also lead to shrunken versions of the proteins responsible for skin development. Less severe mutations result in a collodion membrane and congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE), also known as nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, is a rare type of the ichthyosis family of skin diseases which occurs in 1 in 200,000 to 300,000 births. CIE comes under the umbrella term a ...
-like presentation.
ABCA12 is an ATP-binding cassette transporter
The ATP-binding cassette transporters (ABC transporters) are a transport system superfamily that is one of the largest and possibly one of the oldest gene families. It is represented in all extant phyla, from prokaryotes to humans. ABC tran ...
(ABC transporter), which are members of a large family of proteins that hydrolyze ATP to transport cargo across cell membranes. ABCA12 is thought to be a lipid transporter in keratinocytes
Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells.
Basal cells in the basal layer (''stratum basale'') of the skin are sometimes referre ...
necessary for lipid transport into lamellar granules
In cell biology, lamellar bodies (otherwise known as lamellar granules, membrane-coating granules (MCGs), keratinosomes or Odland bodies) are secretory organelles found in Alveolar cell, type II alveolar cells in the lungs, and in keratinocytes in ...
during the formation of the lipid barrier in the skin.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of harlequin-type ichthyosis relies on both physical examination and laboratory tests. Physical assessment at birth is vital for the initial diagnosis of harlequin ichthyosis. Physical examination reveals characteristic symptoms of the condition especially the abnormalities in the skin surface of newborns. Abnormal findings in physical assessments usually result in employing other diagnostic tests to ascertain the diagnosis. Genetic testing is the most specific diagnostic test for harlequin ichthyosis. This test reveals a loss of function mutation on the ''ABCA12'' gene. Biopsy of skin may be done to assess the histologic characteristics of the cells. Histological findings usually reveal hyperkeratotic skin cells, which leads to a thick, white and hard skin layer.Treatment
Constant care is required to moisturize and protect the skin. The hard outer layer eventually peels off, leaving the vulnerable inner layers of thedermis
The dermis or corium is a layer of skin between the epidermis (with which it makes up the cutis) and subcutaneous tissues, that primarily consists of dense irregular connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. It is divided ...
exposed. Early complications result from infection due to fissuring of the hyperkeratotic
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
plates and respiratory distress
Shortness of breath (SOB), also medically known as dyspnea (in AmE) or dyspnoea (in BrE), is an uncomfortable feeling of not being able to breathe well enough. The American Thoracic Society defines it as "a subjective experience of breathing disc ...
due to physical restriction of chest wall expansion.
Management includes supportive care and treatment of hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
and skin barrier dysfunction. A humidified incubator is generally used. Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Patients are generally anesthetized beforehand. Examples include tracheal intubation, and the balloon tamponade with a Sengstaken-Blake ...
is often required until nares are present. Nutritional support with tube feeds is essential until eclabium
Eclabium means the turning outwards of the lip. Eclabium comes from the Greek word "ek" meaning "out," and the Latin word "labium" meaning "lip." This deformation occurs in most babies born with Harlequin type ichthyosis, caused by genetic defec ...
resolves and infants can begin nursing. Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders.
An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a me ...
consultation is useful for the early management of ectropion
Ectropion is a medical condition in which the lower eyelid turns outwards. It is one of the notable aspects of newborns exhibiting congenital Harlequin-type ichthyosis, but ectropion can occur due to any weakening of tissue of the lower eyelid ...
, which is initially pronounced and resolves as scales are shed. Liberal application of petrolatum
Petroleum jelly, petrolatum, white petrolatum, soft paraffin, or multi-hydrocarbon, CAS number 8009-03-8, is a semi-solid mixture of hydrocarbons (with carbon numbers mainly higher than 25), originally promoted as a topical ointment for its he ...
is needed multiple times a day. In addition, careful debridement
Debridement is the medical removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to improve the healing potential of the remaining healthy tissue. Removal may be surgical, mechanical, chemical, autolytic (self-digestion), and by maggot therapy.
I ...
of constrictive bands of hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologi ...
should be performed to avoid digital ischemia.
Cases of digital autoamputation Autoamputation is the spontaneous detachment (amputation) of an appendage or organ from the body. This is not to be confused with self-amputation. It is usually due to destruction of the blood vessels feeding an extremity such as the finger tips. O ...
or necrosis
Necrosis () is a form of cell injury which results in the premature death of cells in living tissue by autolysis. Necrosis is caused by factors external to the cell or tissue, such as infection, or trauma which result in the unregulated diges ...
have been reported due to cutaneous constriction bands. Relaxation incisions have been used to prevent this morbid complication.
Prognosis
In the past, the disorder was nearly always fatal, whether due todehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water, with an accompanying disruption of metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds free water intake, usually due to exercise, disease, or high environmental temperature. Mil ...
, infection (sepsis
Sepsis, formerly known as septicemia (septicaemia in British English) or blood poisoning, is a life-threatening condition that arises when the body's response to infection causes injury to its own tissues and organs. This initial stage is follo ...
), restricted breathing
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellu ...
due to the plating, or other related causes. The most common cause of death was systemic infection, and sufferers rarely survived for more than a few days. However, improved neonatal intensive care
A neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), also known as an intensive care nursery (ICN), is an intensive care unit (ICU) specializing in the care of ill or premature newborn infants. Neonatal refers to the first 28 days of life. Neonatal care, as kn ...
and early treatment with oral retinoids, such as the drug Isotretinoin
Isotretinoin, also known as 13-''cis''-retinoic acid and sold under the brand name Accutane among others, is a medication primarily used to treat severe acne. It is also used to prevent certain skin cancers (squamous-cell carcinoma), and in th ...
, may improve survival. Early oral retinoid therapy has been shown to soften scales and encourage desquamation. After as little as two weeks of daily oral isotretinoin, fissures in the skin can heal, and plate-like scales can nearly resolve. Improvement in the eclabium and ectropion can also be seen in a matter of weeks.
Children who survive the neonatal period usually evolve to a less severe phenotype, resembling a severe congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma (CIE), also known as nonbullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, is a rare type of the ichthyosis family of skin diseases which occurs in 1 in 200,000 to 300,000 births. CIE comes under the umbrella term a ...
. Patients continue to suffer from temperature dysregulation and may have heat and cold intolerance. Patients can also have generalized poor hair growth, scarring alopecia
Hair loss, also known as alopecia or baldness, refers to a loss of hair from part of the head or body. Typically at least the head is involved. The severity of hair loss can vary from a small area to the entire body. Inflammation or scar ...
, contracture
In pathology, a contracture is a permanent shortening of a muscle or joint. It is usually in response to prolonged hypertonic spasticity in a concentrated muscle area, such as is seen in the tightest muscles of people with conditions like sp ...
s of digits, arthralgias
Arthralgia (from Greek ''arthro-'', joint + ''-algos'', pain) literally means ''joint pain''. Specifically, arthralgia is a symptom of injury, infection, illness (in particular arthritis), or an allergic reaction to medication.
According to MeSH, ...
, failure to thrive
Failure to thrive (FTT), also known as weight faltering or faltering growth, indicates insufficient weight gain or absence of appropriate physical growth in children. FTT is usually defined in terms of weight, and can be evaluated either by a low ...
, hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism (also called ''underactive thyroid'', ''low thyroid'' or ''hypothyreosis'') is a disorder of the endocrine system in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as ...
, and short stature
Short stature refers to a height of a human which is below typical. Whether a person is considered short depends on the context. Because of the lack of preciseness, there is often disagreement about the degree of shortness that should be called ' ...
. Some patients develop a rheumatoid
Rheumatism or rheumatic disorders are conditions causing chronic, often intermittent pain affecting the joints or connective tissue. Rheumatism does not designate any specific disorder, but covers at least 200 different conditions, including art ...
factor-positive polyarthritis
Polyarthritis is any type of arthritis that involves 5 or more joints simultaneously. It is usually associated with autoimmune conditions and may be experienced at any age and is not sex specific.
Causes
Polyarthritis is most often caused by an au ...
. Survivors can also develop fish-like scales and retention of a waxy, yellowish material in seborrheic
Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the ...
areas, with ear adhered to the scalp.
The oldest known survivor is Nusrit "Nelly" Shaheen, who was born in 1984 and is in relatively good health as of June 2021. The maximum lifespan of patients with this disease has not yet been determined with the new treatments.
A study published in 2011 in the Archives of Dermatology concluded: "''Harlequin ichthyosis'' should be regarded as a severe chronic disease that is not invariably fatal. With improved neonatal care and probably the early introduction of oral retinoids, the number of survivors is increasing."
Epidemiology
The condition occurs in roughly 1 in 300,000 people. As an autosomal recessive condition, rates are higher among certain ethnic populations with a higher likelihood of consanguinity.History
The disease has been known since 1750, and was first described in the diary of Rev. Oliver Hart fromCharleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint o ...
:
"On Thursday, April the 5th, 1750, I went to see a most deplorable object of a child, born the night before of one Mary Evans in 'Chas'town. It was surprising to all who beheld it, and I scarcely know how to describe it. The skin was dry and hard and seemed to be cracked in many places, somewhat resembling the scales of a fish. The mouth was large and round and open. It had no external nose, but two holes where the nose should have been. The eyes appeared to be lumps of coagulated blood, turned out, about the bigness of a plum, ghastly to behold. It had no external ears, but holes where the ears should be. The hands and feet appeared to be swollen, were cramped up and felt quite hard. The back part of the head was much open. It made a strange kind of noise, very low, which I cannot describe. It lived about forty-eight hours and was alive when I saw it."The ''harlequin-type'' designation comes from the diamond shape of the scales at birth (resembling the costume of
Arlecchino
Harlequin (; it, Arlecchino ; lmo, Arlechin, Bergamasque pronunciation ) is the best-known of the ''zanni'' or comic servant characters from the Italian ''commedia dell'arte'', associated with the city of Bergamo. The role is traditionally ...
).
Gallery
Notable cases
* Andrea Aberle (1969 - 2021) was 51 years old, making her one of the oldest individuals with harlequin ichthyosis- as well as in general throughout the world, and in the USA in particular. She lived in California with her husband before she passed away from skin related complications. https://www.firstskinfoundation.org/andrea-a-2020 . * Nusrit "Nelly" Shaheen (born in 1984) she resides inCoventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
, England, and was one of nine children in a Pakistani Muslim household. Four of her eight siblings also had the condition but died as young children.
* Ryan Gonzalez (born in 1986) Currently the second oldest person with the condition living in the USA. He was featured in an episode of ''Medical Incredible''.
* Stephanie Turner (1993 – 2017) third oldest in the US with the same condition, and the first ever to give birth. Turner's two children do not have the disease. She died on March 3, 2017, at age 23.
* Mason van Dyk (born 2013), despite being given a life expectancy of one to five days, was five years old as of July 2018. Doctors told his mother Lisa van Dyke that he was the first case of harlequin ichthyosis in South Africa, and that she has a one-in-four chance to have another child with the disease.
* Hunter Steinitz (born October 17, 1994) is one of only twelve Americans living with the disease and is profiled on the National Geographic
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
"Extraordinary Humans: Skin" special.
* Mui Thomas (born in 1992 in Hong Kong) qualified as first rugby referee with harlequin ichthyosis.
* A female baby born in Nagpur
Nagpur (pronunciation: Help:IPA/Marathi, aːɡpuːɾ is the third largest city and the winter capital of the Indian state of Maharashtra. It is the 13th largest city in India by population and according to an Oxford's Economics report, Nag ...
, India in June 2016 died after two days. She is reported as the first case in India.
* Hannah Betts: Born 1990 in Great Britain; died in 2022 at 32 years old.
References
External links
Information
from the U.S.
National Institutes of Health
The National Institutes of Health, commonly referred to as NIH (with each letter pronounced individually), is the primary agency of the United States government responsible for biomedical and public health research. It was founded in the late ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:Harlequin-Type Ichthyosis
Genodermatoses
Autosomal recessive disorders
Rare diseases
Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate